A Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a SWOT Analysis
A Step-By-Step Guide To Performing A SWOT Analysis
Conducting a SWOT analysis is an essential tool for any business looking to stay ahead of its competition. Follow these step-by-step instructions on how to perform a thorough SWOT analysis.
The Ultimate Guide to SWOT Analysis in Strategic Planning
A SWOT analysis is a simple but powerful tool that can help you figure out how to run your business. Whether you’re in the business planning phase or have been in business for years, doing a SWOT analysis is an easy and effective way to come up with smart growth strategies.
What Is SWOT Analysis?
SWOT analysis is a tool used for strategic planning, which stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Your company’s strengths and weaknesses are things you can change and have some control over. Some examples are the people on your team, your patents and other forms of intellectual property, and where you are.
Opportunities and threats are outside of your company. They are things that are happening in the larger market. You can use chances and protect yourself from dangers, but you can’t change them. Some examples are competitors, the prices of raw materials, and the way people shop.
SWOT analysis’ use to assess businesses’ strategic positions before making decisions. It affects Nonprofits, governments, and for-profit corporations. The tool identifies positive and negative factors that may hinder goal achievement. SWOT analysis also needs relevant questions in each area to uncover competitive advantages.
Why do a SWOT Analysis?
If you take the time to do a SWOT analysis, you’ll have a good plan for how to focus on the work you need to do to help your business grow.
You might think you already know everything you need to do to be successful, but a SWOT analysis will force you to look at your business in new ways and from new angles. You’ll look at your strengths and weaknesses and how you can use them to take advantage of the opportunities and threats in your market.
SWOT analysis is a way to test a business’s performance, competition, risk, and potential. It can also be used to check a part of a business, like a product line or division, an industry, or something else.
A SWOT analysis puts together a list of your top strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This list is usually shown as a simple two-by-two grid. If you want to get started right away, you can download our free template.
Who should do a SWOT Analysis?
A SWOT analysis is a critical tool that company founders and leaders should be involved in, as it requires a comprehensive understanding of the business. Yet, it’s also important to gather a diverse group of individuals who can offer unique perspectives on the company. This group should include representatives from sales, customer service, marketing, product development, and even customers themselves. If you’re a solopreneur or small business owner, look to friends, accountants, or vendors for more input.
Existing businesses can use a SWOT analysis to re-evaluate their current strategy and determine potential areas for growth or improvement every 6 to 12 months. For startups, a SWOT analysis is an essential part of the initial business planning process. By evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats from the outset of operations — when resources are often limited — entrepreneurs can make informed decisions about where to focus their attention and resources.
SWOT analysis is a crucial tool that can be used by companies of all sizes to assess their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. For the analysis to yield optimal results, company founders and leaders need to play an active role and not delegate the task to others.
When should you perform a SWOT analysis?
Use a SWOT analysis before committing to any business activity, whether it’s exploring new ideas, changing internal policies, looking for ways to pivot, or changing a plan in the middle of putting it into action. Sometimes it’s a good idea to do a general SWOT analysis to see how your business is doing and make any necessary changes. The analysis can show you where your organization is doing its best work and where it needs to make changes.
Don’t make the mistake of thinking about your business operations in a casual way and hoping that they will all work out on their own. If you take the time to do a formal SWOT analysis, you’ll be able to look at your business as a whole. From there, you can find ways to fix or get rid of your company’s weak points and make the most of its strong points.
Even though the business owner should be involved in making a SWOT analysis, it is often helpful to bring in other team members. Ask different people on the team what they think, and talk about what they say. With all the team’s knowledge, you’ll be able to look at your business from all angles.
You can also do a SWOT analysis for yourself, whether it’s for work or something else.
How to do a SWOT analysis the right way
As mentioned above, you want to gather a team of people together to work on a SWOT analysis. But you don’t need a full-day retreat to do it. A couple of hours should be more than enough.
- Get the right people together
Gather people from different parts of your company and make sure that you have representatives from every department and team as well as experts to help. You’ll find that different groups within your company or outside will have different perspectives that will be critical to making your SWOT analysis successful. The BznsBuilder team has the expertise to help you conduct this strategic planning process, you may book a free consultation
- Put your thoughts up on the wall
Doing a SWOT analysis is like having a meeting to come up with ideas, and there are right and wrong ways to do both. it would be best to give everyone a pad of sticky notes and let them come up with ideas on their own. This stops people from thinking like a group and makes sure that everyone hears.
After 5–10 minutes of thinking on your own, put all the sticky notes on the wall and group ideas that are similar. Let anyone add more notes if someone else’s idea makes them think of something new.
- Put the ideas in order
After putting all the ideas in order, it’s time to rank them. I like voting systems where each person gets five or ten “votes” that they can give out if they want. For this part of the exercise, it helps to have different colored sticky dots.
After the voting, you should have a list of ideas in order of how important they are. The list can now talk about and debated, and someone in the room should be able to make the final decision about the order of importance. Most of the time, this is the CEO, but it could also be someone else in charge of business strategy.
Follow this method to come up with ideas for each of your SWOT analysis’s four quadrants: strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Elements of a SWOT Analysis
Every SWOT analysis will look at these four things. Even though each company will find different things in each of these categories, a SWOT analysis is not complete without all the following:
Strengths
Strengths are the things that a company does well and that set it apart from its competitors. For example, a strong brand, a loyal customer base, a strong balance sheet, unique technology, and so on. For example, a hedge fund may have made its own trading strategy that does better than the market. Then, it has to decide how to use those results to get more investors.
Weaknesses
When an organization has weaknesses, it can’t do as well as it could. They are areas where the business needs to improve to stay competitive: a weak brand, a higher-than-average turnover, high levels of debt, an inefficient supply chain, or a lack of capital.
Opportunities
Opportunities are good things in the outside world that could give a business an edge over its competitors. For example, if a country lowers its tariffs, a car company can sell more cars in a new market and get a bigger share of that market.
Threats
Threats are things that could cause problems for an organisation. For example, a drought is a threat to a company that grows wheat because it can hurt or destroy the crop. Other common threats include things like the price of materials going up, the amount of competition going up, the lack of workers, etc.
How do you write a SWOT analysis that is good?
To make a SWOT analysis, you need to figure out what a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats are and analyse them. It’s best to start by making a list of questions for each element. The questions help you figure out how to do the SWOT analysis and make a list that is fair. The SWOT framework can be made as a list, as free-form text, or, most often, as a four-cell table with one quadrant for each element. First, come the strengths and weaknesses, then the opportunities and threats.
Compile Ideas: Questions that can help spark ideas
The group of people tasked with doing the SWOT analysis should start making a list of ideas for each of the four parts of the analysis. In the table below are some questions to ask or things to think about for each group.
Here are some questions you can ask your team as you build your SWOT analysis. These questions can help you understand each section and get your mind going in new directions.
Internal Factors
What happens inside the company is a great source of information for the strengths and weaknesses parts of the SWOT analysis. Financial and human resources, tangible and intangible (brand name) assets and operational efficiencies are all examples of internal factors.
Strengths
Your company’s strengths are the good things that are already inside the company. These are things you can do something about.
- What kinds of business processes work well?
- What are the strengths of your teams? (Knowledge, education, network, skills, and reputation) – What physical assets do you have, like customers, equipment, technology, cash, and patents?
- What do you have that makes you better than your competitors?
Weaknesses
Weaknesses are negative things that make your strengths less impressive. You might need to get better at these things to be competitive.
- Does your business need anything to stay in the game?
- What parts of the business need to be improved?
- Does your business need money or equipment that can be seen or touched?
- Does your team have any holes?
- Is where you live the best place for your success?
External Factors
What goes on outside of a company is as important to its success as what goes on inside of it. You can use categories like monetary policies, changes in the market, and access to suppliers to make a list of your strengths and weaknesses.
Opportunities
Opportunities are things outside of your business that are likely to help you be successful.
- Is your market growing, and are there any trends that will make people want to buy more of what you’re selling?
- Are there any events coming up that your company could use to grow the business?
- Will there be changes to regulations that could be good for your business?
- Do customers think well of you if your business is up and running?
Threats
Threats are things that come from the outside and that you can’t change. You might want to think about making plans for how to deal with them if they happen.
- Do you have competitors who might want to get into your market?
- Will your suppliers always be able to give you the raw materials you need at the prices you need?
- Could changes in technology in the future change the way you do business?
- Is there a change in the way people act that could hurt your business?
- Are there any market trends that could be dangerous?

Companies may want to do this step as a “white-boarding” or “sticky note” session. or even use planning tools like BznsBuilder to guide them.
The idea is that there is no right or wrong answer, and everyone should be encouraged to share their ideas. These ideas can be thrown out later. For now, the goal should be to come up with as many things as possible that will make other people creative and inspired.
SWOT Analysis Example
All the SWOT analysis examples and templates shown below can be made online using the SWOT analysis section of the BznsBuilder tool.
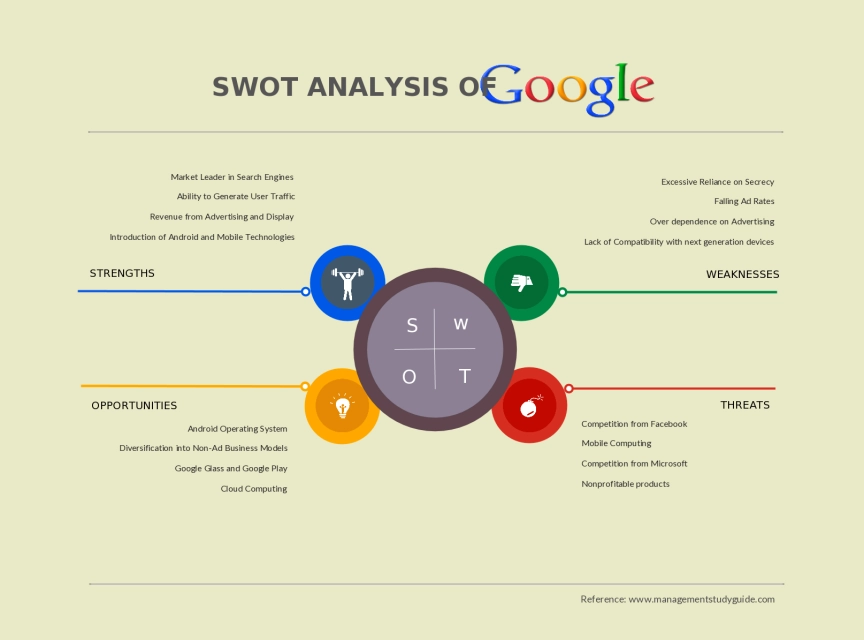
SWOT Analysis Template of Google, Alphabet. Inc
This is a SWOT analysis of Google, Alphabet’s most popular search engine. As the most used search engine in the world, Google has to deal with market opportunities and competition to keep its business going. This SWOT analysis of Google is a good example of a model analysis for a very large company.
NIKE SWOT Analysis Template
This SWOT analysis of NIKE is a summary of the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This SWOT analysis template can be used by any brand, no matter how well-known it is or how new it is to the market. It can be used to look at the internal and external factors that could affect the brand’s authority and growth in the market.

SWOT Analysis Template of Facebook
This is Facebook’s SWOT analysis. Facebook is now one of the most popular social media sites in the world. It has more than 1 billion users. A SWOT analysis like the one below can be used to figure out how they compare to their competitors right now. It also helps them come up with new ways to boost the authority of their brand in the market.

Amazon Inc. SWOT Analysis Template
Amazon is one of the most well-known cloud computing and online shopping sites in the world. With the rapid growth of the eCommerce and cloud computing industries, Amazon now has to deal with a lot of competition from a lot of other companies. A SWOT analysis like this is very helpful for Amazon and any other company in this situation because it helps them come up with new ways to stay ahead of the competition and deal with problems in their way.

SWOT Analysis Template of McDonald’s
Here is a SWOT analysis for McDonald’s in the shape of a tasty burger. As a well-known chain of fast-food hamburger restaurants around the world, it has to keep up its brand name in more than 119 countries. Analyzing their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a great way to keep their popularity with such a large number of customers. A study like this will help them figure out what they should change and what they should get rid of to keep their customers happy.

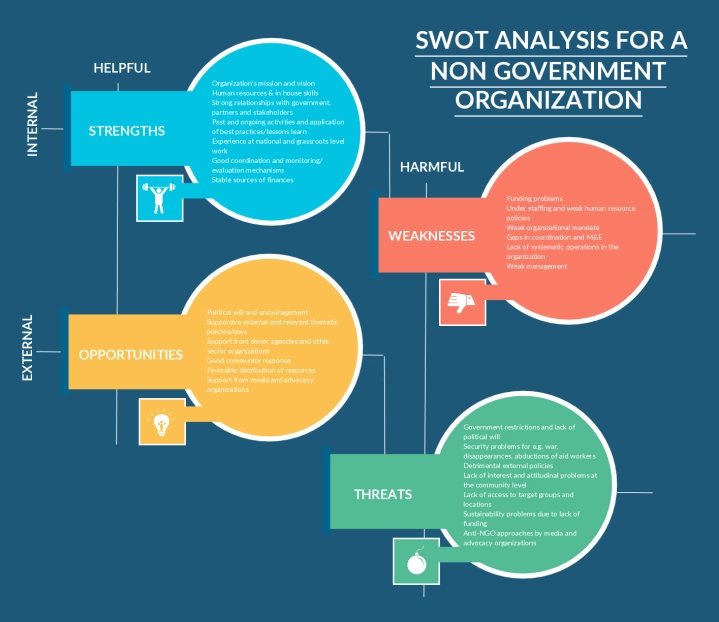
SWOT Analysis Template for Non-Governmental Organization
Not sure what a SWOT diagram is? Here is a SWOT diagram that has some real information in it. Check how they are listed and make your own SWOT diagram.
How to Avoid the 5 Most Common SWOT Analysis Mistakes
SWOT is one of the best ways to figure out if a project is likely to work or not. It’s strong enough to tell what’s wrong with a business. But if you don’t do it right, it can give you the wrong information and waste your time and money. Here are some common mistakes people make with SWOT analysis and what you can do to avoid them.
1- Adding Long Lists
Most likely, the most common SWOT analysis mistake is to write down too many things. This usually happens when there isn’t a clear goal or a well-defined scope. The SWOT analysis is made by many people in an organisation, and long lists make it harder to figure out what’s important and what’s not.
How to fix it: Make it clear why you’re doing a SWOT analysis and what you want to get out of it. Keep each section to 3–5 important points.
2- Overestimating Strengths
Let’s face it, this is something that most of us do. Every company that makes software thinks its developers are the best, and every hotel thinks its chefs are the best. But that’s rarely the case.
When everyone is fresh and ready to help, strengths are often the first thing added to the SWOT. So it’s very easy to use strengths too much. Point 1 is a bit helpful here. Because you only have 3-5 points, you have to think a bit more about what to include. Still, it’s easy to overestimate your strengths, which can hurt your project when it’s put into action.
How to fix it: Take a good look at your strengths. If you need to, ask outsiders for their honest opinions. If it’s a product or service, try to see it from the customer’s point of view. Will they think it gives you an advantage over your competitors?
3- Generalizing Factors
A mistake that is less obvious but very dangerous in a SWOT analysis. For example, if you run a software company, “long release cycle” could be a weakness. It’s clear that it’s a weakness, but it’s hard to come up with a good plan based on that. Several things could cause it to be late.
But if you added that factor as “not enough QA resources,” anyone who looks at the diagram can see the problem right away and take steps to fix it.
How to Fix: Don’t lump factors together and try to include cause or reason as a factor. Also, make sure to add numbers whenever you can.
4- Not Talking About Weaknesses
Almost no one likes to admit they have weaknesses. It’s even harder when you’re on a high after figuring out your most important strengths during a SWOT analysis. In a business setting, it’s even harder because no one wants to show weakness to their boss.
Yet, underestimating your weaknesses can be more dangerous than overestimating your strengths.
How to fix it: Be honest about your flaws. Encourage people to come up with weaknesses and assure them that it won’t be held against them. If many are participating you can ask each person to list down weaknesses and then pick the most important ones from them.
5- Ignoring PESTLE Analysis
A PESTLE analysis looks at the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that have the most impact on an organisation. It can be used in a variety of situations and can help senior managers and people professionals make strategic decisions.
Different problems can be caused by both opportunities and threats. Since strengths and weaknesses are things that come from the inside, they are pretty easy to figure out and list. Not so easy because opportunities and threats come from the outside.
PESTLE analysis is a standard and structured way for businesses to look at these outside factors. People often get SWOT analysis and PESTLE analysis mixed up. And businesses that don’t pay attention to it could miss out on great opportunities or start to see opportunities where there aren’t any.
How to fix it: Do a proper PESTLE analysis and use that analysis to pick your opportunities and threats.
How to use your SWOT Analysis
Now that you’ve finished your SWOT analysis, you’re ready to turn it into a real plan. After all, the point of the exercise is to come up with a plan you can work on over the next few months.
The first step is to think about your strengths and how you can use them to make the most of your chances. Then, think about how your strengths can help you deal with market threats. You can use this analysis to make a list of things you can do.
With your list of things to do in hand, look at your company’s calendar and start putting goals (or milestones) on it. What do you want to get done every three months (or a month) from now on?
You can also do this by thinking about how opportunities from the outside world might help you deal with your own internal weaknesses. Can you also make these weaknesses less of a problem so you can avoid the threats you found?
Again, you’ll have a list of things to do that you’ll need to rank and plan.
Steps to take after your SWOT analysis
With your goals and actions in hand, you’ll be well on your way to making a business plan. At BznsBuilder we prefer to use the Lean Planning method for both business planning and strategic planning. The actions you come up with from your SWOT analysis will fit right into the milestones section of your Lean Plan and give your business a solid base from which to grow. You can get free access to our Lean Plan tool to help you get started.








